Network Concepts Basics
Learn the basics of netwroking
Networking Concept
Mac address
- Media control access
- It is physical address to identify the devices
- it identify the NIC of each divices (NIC–> Network identification card)
- ex:- ether 00:0c:49:0a:43:03
- Mac work in the second and third layer of the OSI model
- Specially it is related to the switches
TCP –VS– UDP
TCP
- Transmission COntrol Protocol
- Connection oriented protocol
- used in HTTPS/SSH/TelNet/SMTP/FTP
- provide the more security and relailablity
- it form one-to-one connection and it gurantee the complete delivery of data
- Three way hand shake
- SYN -> SYN-ACK -> ACK
- it is slow due to three-way-handshake, it take time to complete and establis the connection
- Use port to establish the connection
- During hand-shake it acknowldge your machine to the requested server
- contains the 20Byte packet
UDP
- User Datagram Protocol
- Connection less Protocol
- it provide the fast transmission
- Broadcast or multicast the message and the complete delivery of data is note guarnted
- Streamming on voice-over-io(VOIP), DHCP,DNS
- Used for streaming the data like procast, video
- contains the 8Byte packet
Comman Ports and Protocol
TCP
PROTOCOL/SERVICE PORT'S
FTP 21
SSH 22
TelNet 23
SMTP 25
DNS 53
HTTP/HTTPS 80/443
POP3 110
SMB 139+445
IMAP 143
UDP
PROTOCOL/SERVICE PORT'S
DNS 53
DHCP 67.68
TFTP 69
SNMP 161
The OSI Model
Open Systems Interconnection(OSI)
Learn this mnemonic to to know the seven layer sequence
Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away
OSI seven layers are
1. Physical (P)Please 2. Data link (D)Do 3. Network (N)Not 4. Transport (T)Throw 5. Session (S)Sausage 6. Presentation (P)Pizza 7. Application (A)AwayOSI Model Explain REF
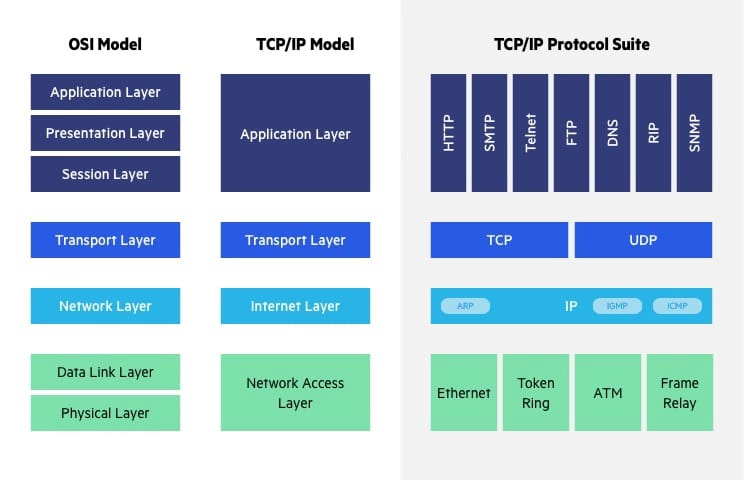
Layers For
1. Physical -- Provide the connection between computer and network, it includes physical datacable,server
2. Data Link -- Make sure the data-transfer is error-free between different node, when data packet arrive at network layer then data link layer(DLL) deliver that packet to the requested host using MAC address.
3. Network -- Transmitt the data from one host to other, in different netwroks.It also place the reciver/sender ip address in header of packet.
4. Transport -- Data packet referred as Segment, it is responsible for the end-to-end delivery of complete message without any error/packet loss.
5. Session -- Responsible for the establishing the session,maintaining and also ensure the security
6. Presentation --- Data from application layer(layer 7) is extracted here and manipulate as per the required to transmit over network.
7. Application --- Used by the end user software such as web browser and email clients.
While Receiving the data from network model work from layer 1 –> layer 7
While sending the data from machine model work from layer 7 –> layer 1
Networks
IP address are work with the third layer of the OSI Model
There are two types of ip address
- IPv4 : 192.168.34.123
- IPv6 : 23:s3:3w:34:dw:23:2d
In IPv4 each section after delimeter(.) is contain the 8 bits each (0 & 1)
The total of complete ip address is 32 byte.
the total in terms of the bits is 256 that is from 0 to 255.
There are many network around you and your system and all are having the very specific identity number that is known as IP address.
Types of ip address in a network
Class Start ip End ip Subnet Mask Netwroks(max) Hosts(max) A 0 127 255.0.0.0 126 16,646,144 B 127 191 255.255.0.0 16,383 15,024 C 192 223 255.225.255.0 2097,151 254 IP address in the binary format
- 11111111.11111111.11111111.0 == 255.255.255.0
- == 192.168.15.
Some Standard Slash Network
- /24 Network
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 - /25 Network
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
- /24 Network
Links
It is getting hard for me to write and draw the ahed so i am adding some link of my document go through them, Some link to internet resources